No products
Chenonceau
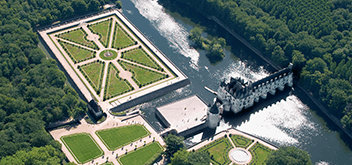
 Built over the river Cher, with its unique beauty reflected in the water, the castle of Chenonceau is one of the jewels of the Loire Valley. During over 400 years of its history, various famous ladies built Chenonceau and have lived in it.. Amongst these ladies were: Catherine Briçonnet, wife of Thomas Bohier, the first builder; Diane de Poitiers, a favourite of Henry II; the Queen Regent Catherine de Médicis; her daughter-in-law, Louise de Lorraine, the unconsolable widow of Henry III, Gabrielle d'Estrées, a favourite of Henry IV; Madame Dupin, hostess of the young Jean-Jacques Rousseau and Madame Pelouze, who restored the castle at the end of the XIXth century. In the Dômes building, there is a wax museum in their honour. Delightful factors of the site are the French gardens and the park that surrounds it, giving the place a graceful and delicate impression. Chenonceau is not only known for its architecture and history, but also for the richness of its collections, as one sees when visiting the interior. There's furniture of the Renaissance period, an important assembly of carpets of the XVIth and XVIIth centuries and numerous paintings of masters, including chose of le Primatice, le Corrège, Rubens, le Tintoret, Rigaud, Nattier, and Van Loo...
Built over the river Cher, with its unique beauty reflected in the water, the castle of Chenonceau is one of the jewels of the Loire Valley. During over 400 years of its history, various famous ladies built Chenonceau and have lived in it.. Amongst these ladies were: Catherine Briçonnet, wife of Thomas Bohier, the first builder; Diane de Poitiers, a favourite of Henry II; the Queen Regent Catherine de Médicis; her daughter-in-law, Louise de Lorraine, the unconsolable widow of Henry III, Gabrielle d'Estrées, a favourite of Henry IV; Madame Dupin, hostess of the young Jean-Jacques Rousseau and Madame Pelouze, who restored the castle at the end of the XIXth century. In the Dômes building, there is a wax museum in their honour. Delightful factors of the site are the French gardens and the park that surrounds it, giving the place a graceful and delicate impression. Chenonceau is not only known for its architecture and history, but also for the richness of its collections, as one sees when visiting the interior. There's furniture of the Renaissance period, an important assembly of carpets of the XVIth and XVIIth centuries and numerous paintings of masters, including chose of le Primatice, le Corrège, Rubens, le Tintoret, Rigaud, Nattier, and Van Loo...
The original manor was torched in 1411 to punish owner Jean Marques for an act of sedition. He rebuilt a castle and fortified mill on the site in the 1430s. Subsequently, his indebted heir Pierre Marques sold the castle to Thomas Bohier, Chamberlain for King Charles VIII of France in 1513. Bohier destroyed the existing castle and built an entirely new residence between 1515 and 1521; the work was sometimes overseen by his wife Katherine Briçonnet, who delighted in hosting French nobility, including King Francis I on two occasions. Eventually, the château was seized from Bohier's son by King Francis I of France for unpaid debts to the Crown; after Francis' death in 1547, Henry II offered the château as a gift to his mistress, Diane de Poitiers, who became fervently attached to the Chateau and its view along the river. She would have the arched bridge constructed, joining the Chateau to its opposite bank. She then oversaw the planting of extensive flower and vegetable gardens along with a variety of fruit trees. Set along the banks of the river, but buttressed from flooding by stone terraces, the exquisite gardens were laid out in four triangles.
Eventually, the château was seized from Bohier's son by King Francis I of France for unpaid debts to the Crown; after Francis' death in 1547, Henry II offered the château as a gift to his mistress, Diane de Poitiers, who became fervently attached to the Chateau and its view along the river. She would have the arched bridge constructed, joining the Chateau to its opposite bank. She then oversaw the planting of extensive flower and vegetable gardens along with a variety of fruit trees. Set along the banks of the river, but buttressed from flooding by stone terraces, the exquisite gardens were laid out in four triangles.
Diane de Poitiers was the unquestioned mistress of the castle, but ownership remained with the crown until 1555, when years of delicate legal maneuvers finally yielded possession to her. However, after King Henry II died in 1559, his strong-willed widow and regent Catherine de' Medici had Diane expelled. Because the estate no longer belonged to the crown, she could not seize it outright, but forced Diane to exchange it for the Chateau of Chaumont. Queen Catherine then made Chenonceau her own favorite residence, adding a new series of gardens.
 As Regent of France, Catherine would spend a fortune on the château and on spectacular nighttime parties. In 1560, the first ever fireworks display seen in France took place during the celebrations marking the ascension to the throne of Catherine's son Francis II. The grand gallery, which extended along the existing bridge to cross the entire river, was dedicated in 1577.
As Regent of France, Catherine would spend a fortune on the château and on spectacular nighttime parties. In 1560, the first ever fireworks display seen in France took place during the celebrations marking the ascension to the throne of Catherine's son Francis II. The grand gallery, which extended along the existing bridge to cross the entire river, was dedicated in 1577.
On Catherine's death in 1589 the château went to her daughter-in-law, Louise de Lorraine-Vaudémont, wife of King Henry III. At Chenonceau Louise was told of her husband's assassination and she fell into a state of depression, spending the remainder of her days wandering aimlessly along the château's vast corridors dressed in mourning clothes amidst somber black tapestries stitched with skulls and crossbones.
Another mistress took over in 1624, when Gabrielle d'Estrées, the favorite of King Henry IV, inhabited the castle. After that, it was owned by Louise's heir César of Vendôme and his wife, Françoise of Lorraine, Duchess of Vendôme, and passed quietly down the Valois line of inheritance, alternately inhabited and abandoned for more than a hundred years.
Chateau de Chenonceau was bought by the Duke of Bourbon in 1720. Little by little, he sold off all of the castle's contents. Many of the fine statues ended up at Versailles. The estate itself was finally sold to a squire named Claude Dupin.
 Claude's wife (daughter of financier Samuel Bernard and grandmother of George Sand), Madame Louise Dupin, brought life back to the castle by entertaining the leaders of The Enlightenment: Voltaire, Montesquieu, Buffon, Bernard le Bovier de Fontenelle, Pierre de Marivaux, and Jean-Jacques Rousseau. She saved the Chateau from destruction during the French Revolution, preserving it from being destroyed by the Revolutionary Guard because it was essential to travel and commerce, being the only bridge across the river for many miles. She is said to be the one who changed the spelling of the Chateau (from Chenonceaux to Chenonceau) to please the villagers during the French Revolution. She dropped the "x" at the end of the Chateau's name to differentiate what was a symbol of royalty from the Republic. Although no official sources have been found to support this legend, the Chateau has been since referred to and accepted as Chenonceau.
Claude's wife (daughter of financier Samuel Bernard and grandmother of George Sand), Madame Louise Dupin, brought life back to the castle by entertaining the leaders of The Enlightenment: Voltaire, Montesquieu, Buffon, Bernard le Bovier de Fontenelle, Pierre de Marivaux, and Jean-Jacques Rousseau. She saved the Chateau from destruction during the French Revolution, preserving it from being destroyed by the Revolutionary Guard because it was essential to travel and commerce, being the only bridge across the river for many miles. She is said to be the one who changed the spelling of the Chateau (from Chenonceaux to Chenonceau) to please the villagers during the French Revolution. She dropped the "x" at the end of the Chateau's name to differentiate what was a symbol of royalty from the Republic. Although no official sources have been found to support this legend, the Chateau has been since referred to and accepted as Chenonceau.
In 1864, Daniel Wilson, a Scotsman who had made a fortune installing gaslights throughout Paris, bought the château for his daughter. In the tradition of Catherine de' Medici, she would spend a fortune on elaborate parties to such an extent that her finances were depleted and the Chateau was seized and sold to José-Emilio Terry, a Cuban millionaire, in 1891. Terry sold it in 1896 to a family member, Francisco Terry, and in 1913, the Menier family, famous for their chocolates, bought the Chateau and still own it to this day.
During World War I the gallery was used as a hospital ward; during the Second War it was a means of escaping from the Nazi occupied zone on one side of the River Cher to the "free" Vichy zone on the opposite bank.
In 1951, the Menier family entrusted the Chateau's restoration to Bernard Voisin, who brought the dilapidated structure and the gardens (ravaged in the Cher River flood in 1940) back to a reflection of its former glory.
An architectural mixture of late Gothic and early Renaissance, are open to the public. Other than the Royal Palace of Versailles, Chenonceau is the most visited Chateau in France.